In my quest for finding a cheapest off-the-shelf linux h/w, I came across this 5Euro device capable of running open-source linux OS(openwrt). I was delighted to see this tiny little device(A5-V11-router) consuming just around 0.3Watts - this is a perfect piece of h/w for IoT application.
Here are some interesting facts about this little device(A5-V11-router).
1)100Mbit Ethernet port
2)IEEE802.1b/g/n wifi interface
2)An usb port for attaching peripheral device
4)360Mhz Mips CPU(Ralink RT5350)
5)32Mb SDRAM
6)4Mb flash.
7)red and blue LED for showing different status.
It was intended to be used as an internet-hotspot in combination with usb-3g-dongle and simcard. But, for my use, i have overwritten OEM fmw with my own customized openwrt(a5v11-xmpp) image which can be downloaded from here.
Q: what is the purpose of customized a5v11-xmpp image?
Ans: in this image, I have stripped down most of the router/wifi functionality to accomodate an xmpp-chat-client-daemon(lib-gloox based) to act as a chat-bot. Xmpp makes it easy to access your home network without tweaking your home router settings(e.g:port-opening/NAT etc). You dont need to expose any ports of your home-broadband-router to the internet.
Overwrite OEM firmware of a5-v11-router with a5v11-xmpp image and keep this little piece connected to your home internet so that you can "chat" with your h/w even when you are outside of home network.
Setup Instructions:
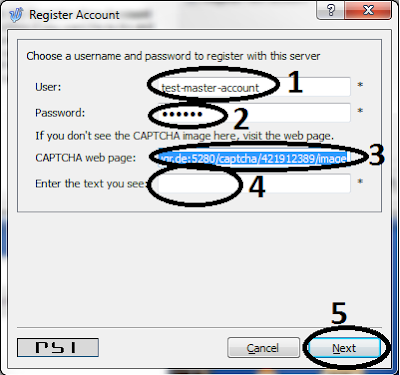
Step-1: Xmpp master/slave account creation.
As explained here, you need to prepare two xmpp/jabber accounts on your favorite jabber-server. and let these two accounts be "friends" so that xmpp-server can pass the messages between these two accounts.
Step-2: connect CAT-5/6 cable between your pc and a5-v11-router and power ON the router.
Step -3: Overwrite Stock Firmware with openwrt based a5v11-xmpp-image
On openwrt wiki there are instructions about how to overwrite stock firmware with openwrt-firmware. For overwriting the stock firmware with a5v11-xmpp-image, you can follow a step-by-step guide as detailed here in my other blog.
Step-6: login to host "my-a5v11" using ssh/putty (user: root | pw: brb0x)
Step-7: prepare login details (This step is redundant as it is already explained in step-3)
echo "user: test-slave-account@xabber.de" >/etc/xmproxy/xmpp-login.txt; echo "pw: chatbotpw">>/etc/xmproxy/xmpp-login.txt ; reboot
Note: in above command, replace test-slave-account details with your own user/pw. (also use passwd command to change the default root password(brb0x) to your own)
Step-8: prepare your smart phone with xabber app and login using test-master-account username and password.
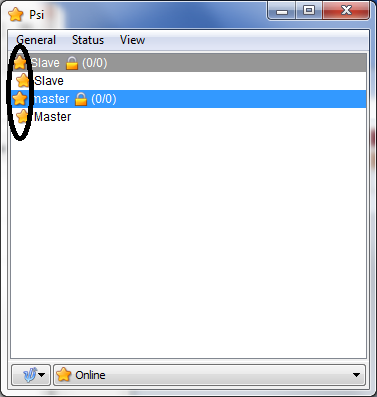
Step-9: you will see that your a5-v11-router is online on your smart-phone's xabber app.
Step-10: type "help" and send the message to a5-v11-router, you will get the reply with list of available commands.
Q: Ok, what now? i have this tiny little device sitting next to my home router consuming 0.3w, what next? what can i do with it? can you give some examples?
Ans: here are some commands that makes this device useful.
1)From your smart-phone(no matter where u r in the word, as long as your phone is on internet) send "publicip" chat message and you get the response from chat-bot showing public-ip of your home router, this helps you to be independent of dynamic-dns setup, you can always see public-ip using xabber app.
2)connect i2c-tiny-usb (as shown in the picture below) to generate i2c from USB port of a5-v11-router, with i2c you can control/read many pheripheral chips ex: temp/humidity sensor, power sensor, gpio relay-control(use your imagination for home automation with i2c).
send "shellcmd i2cdetect -r -y 0" and wait for "return=Success" message, and then read the output of last triggered shell command using "shellcmdresp" to see what i2c devices were detected.
ex: use "shellcmd i2cset -f -y 1 0x3c 0x00 0xff b" to make all pins of PCF8574 high.
3)Control sonoff wifi relays having tasmota firmware. ex: In your home network, if there is a sonoff relay at ip 192.168.1.10, send the following commands to chat-bot for controlling the relay(chat-bot uses http GET commands to control sonoff relays).
a)"sonoff 192.168.1.10 on" - switches ON the relay.
b)"sonoff 192.168.1.10 off" - switches OFF the relay.
c)"sonoff 192.168.1.10 toggle" - toggles the relay.
d)"sonoff 192.168.1.10" - reads the current state of relay.
Note: Incase if sonoff relay has a hostname, replace the ip with hostname in the example above.
d)"sonoff 192.168.1.10" - reads the current state of relay.
Note: Incase if sonoff relay has a hostname, replace the ip with hostname in the example above.
4)on your network if there are linux pc's, you can trigger remote commands via sshpass of the chat-bot. Here is an example..
a)"shellcmd sshpass -praspberry ssh -y pi@raspi-ip sudo reboot" would reboot raspi.
b)"shellcmd sshpass -praspberry ssh -y pi@raspi-ip sudo poweroff" would switch off raspi.
c)"shellcmd sshpass -praspberry ssh -y pi@raspi-ip omxplay /tmp/video.mp4" would start playing mp4 video.
5)send etherwake command to turn on a PC which was already in WoL mode, ex:
a)"shellcmd etherwake 00:00:DE:AD:BE:EF" (replace the MAC id with actual one)
watch-out this blog for for more use cases...
Q: I dont trust your ready to use image, I need to know the details, where are the sources? how can i create the image myself?
Ans: Here is the link to sources and build instruction so that you can create your own trusted image.